Misalignment in Semantic User Model Elicitation via Conversational Agents: A Case Study in Navigation Support for Visually Impaired People
International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction 38(18-20):1909-1925, 2022
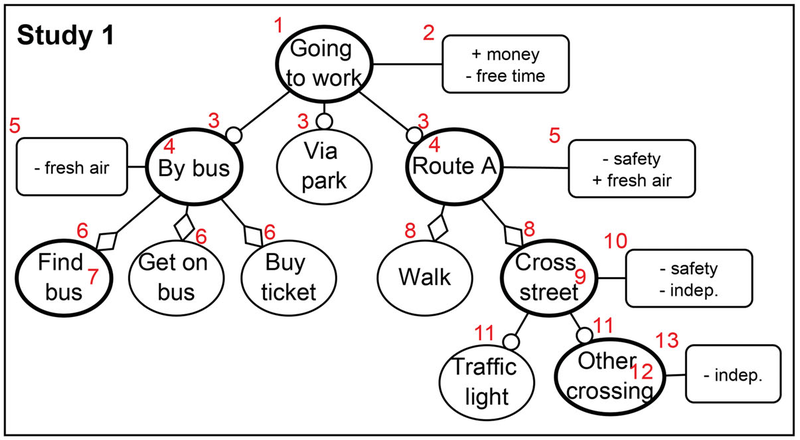
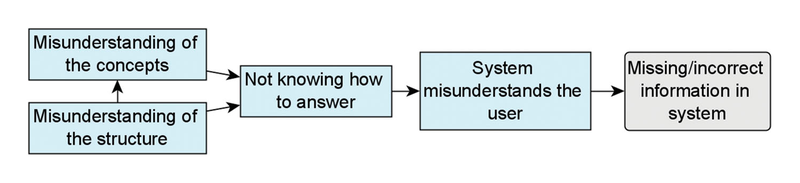
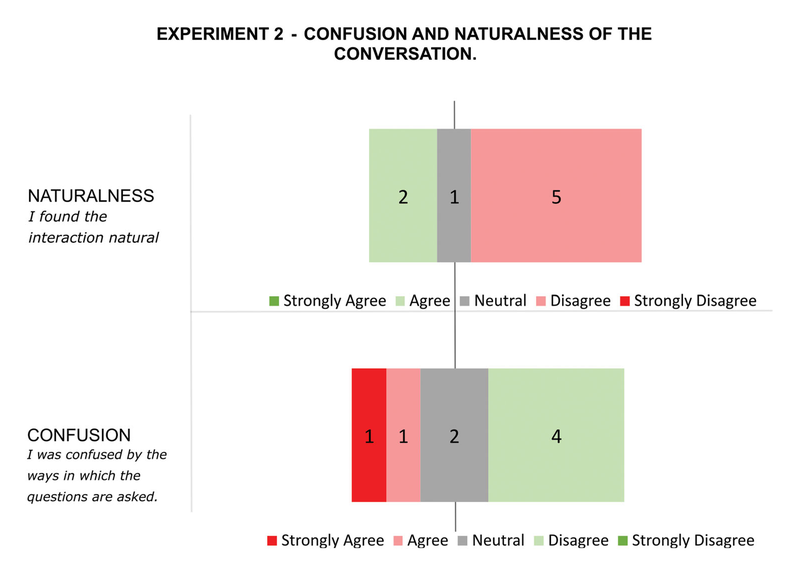
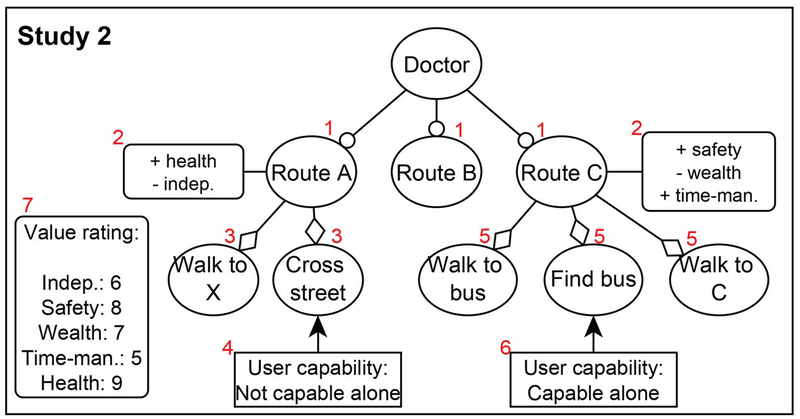
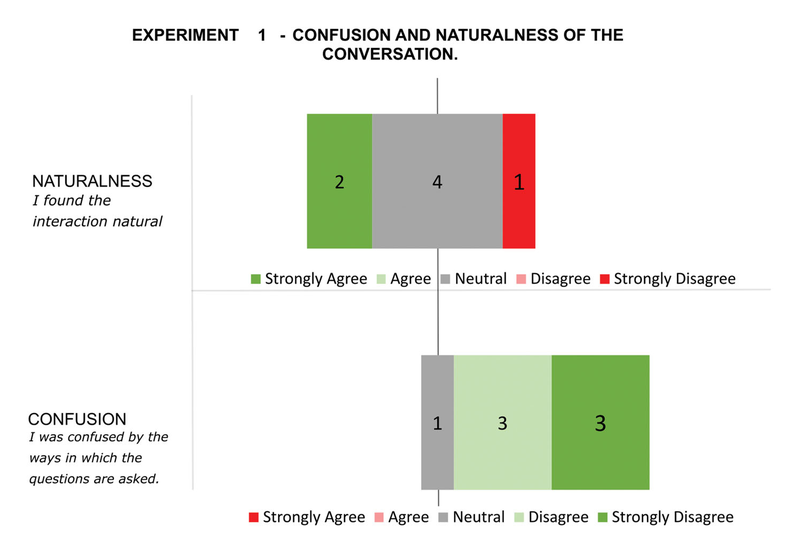
Disabled people can benefit greatly from assistive digital technologies. However, this increased human-machine symbiosis makes it important that systems are personalized and transparent to users. Existing work often uses data-oriented approaches. However, these approaches lack transparency and make it hard to influence the system's behavior. In this paper, we use knowledge-based techniques for personalization, introducing the concept of Semantic User Models for representing the behavior, values and capabilities of users. To allow the system to construct such a user model, we investigate the use of a conversational agent which can elicit the relevant information from users through dialogue. A conversational interface is essential for our case study of navigation support for visually impaired people, but in general, has the potential to enhance transparency as users know what the system represents about them. For such a dialogue to be effective, it is crucial that the user understands what the conversational agent is asking, i.e., that misalignments that decrease the transparency are avoided or resolved. In this paper, we investigate whether we can use a conversational agent for Semantic User Model elicitation, which types of misalignments can occur in this process and how they are related, and how misalignments can be reduced. We investigate this in two (iterative) qualitative studies (n=7 and n=8) with visually impaired people in which a personalized user model for navigation support is elicited via a dialogue with a conversational agent. Our results show four hierarchically structured levels of human-agent misalignment. We identify several design solutions for reducing misalignments, which point to the need for restricting the generic user model to what is needed in the domain under consideration. With this research, we lay a foundation for conversational agents capable of eliciting Semantic User Models.